(Program Image from NIH website)
前言
隨定序技術的發展演進,定序分析已從單一樣本的探討、家族segregation analysis,擴展至大規模族群分析的階段。近年來已有許多國家或計畫組織,積極地針對群體健康,建立具價值的人體生物資料庫: UK Biobank, gnomAD, 或 Taiwan Biobank 等結果林立,並實際應用至臨床研究。今日要介紹的定序計畫,是由美國 National Institutes of Health (NIH) 主持的 All of Us Research Program,本文內容包含計畫簡介,收案狀況與近期成果。
計畫簡介
All of US 起源於 2015 美國發起之精準醫療計畫 (Precision Medicine Initiative),針對美國多元族群進行大規模的資料收集與討論
All of Us is working to improve health care through research. Unlike research studies that focus on one disease or group of people, All of Us is building a diverse database that can inform thousands of studies on a variety of health conditions. This creates more opportunities to:
- Know the risk factors for certain diseases
- Figure out which treatments work best for people of different backgrounds
- Connect people with the right clinical studies for their needs
- Learn how technologies can help us take steps to be healthier
從官網的簡介可知多元族群與資料類型為計畫核心,也勢必是基因體分析的發展趨勢
計畫特點
大規模的樣本收案
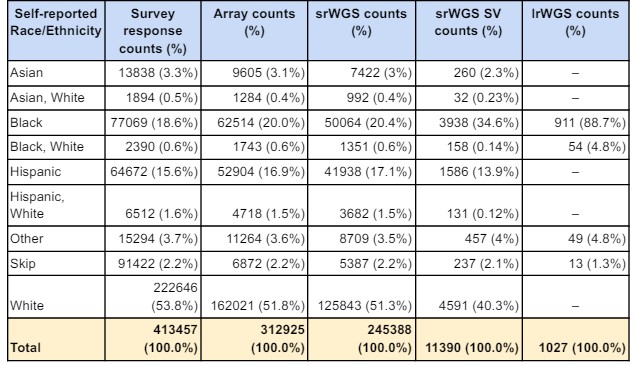
美國幅員廣闊,又因歷史發展族群多元,使收案數量大族群多元。至2024年4月已有近80萬人註冊網站,近55萬人完成初步收案與調查,根據官方釋出(來自問卷)的族群統計,非歐洲族群的比例大幅提高。

下表為2024最新研究成果所公布的資料類別與族群樣本數,其實可發現擁有完整WGS資料的比例仍佔少數,並持續提升
多元資料類型
問卷收集資訊包含基本生活習慣,還有因應前幾年COVID-19的追蹤。有些問題很有趣: 像是社交軟體帳號、管制藥品使用史(列出許多毒品名稱,還有正在服用的選項)、社區環境狀況等,和 Taiwan Biobank 相比,多收集許多環境與心理健康的資訊。族群詢問上相當詳細,依地區劃分後再分國家,如Asian下可再勾選Asian Indian, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese… 以協助 PCA clustering 或model training 時做特徵依據
除了問卷調查,All of US 也收集許多來源的個人資料:
- 生物檢體(biosamples): blood, saliva, and/or urine sample 主要進行定序分析
- 電子病例紀錄(electronic health records,EHR): 收集樣本相關疾病與生理測量數值,在前面 Data Broswer 網站也有釋出部分統計結果,資料使用前會經由 Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) 進行術語轉換與數據標準化
- 體檢數值(physical measurement): 參與者可至合作醫院進行檢查,量測身高、體重、血壓等
- 穿戴式裝置紀錄: 與Fitbit合作,當使用者同意共享紀錄,即可獲得如心跳、運動與睡眠狀態等監測數值
目前收集狀況穩健,引述自最新發表文章:
99% of participants with WGS data also have survey data and physical measurements, and 84% also have EHR data.
具一定準確度的分析架構
All of US 以多元平台定序(short-read whole genome sequencing, long-read whole genome sequencing, and genome-wide genotyping arrays),並偵測個體與族群階層的變異,分析流程皆以GIAB truth set與標準品衡量準確度
以 short-read WGS sequencing data 分析為例:
- PCR-free barcoded Illumina Kapa HyperPrep kit
- sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 instrument
- GRCh38dh as reference
- Illumina DRAGEN v3.4.12 for preprocessing and variant calling,當時使用的command line 有公布在 illumina 官網
- QC measures for each steps
- annotation using using Illumina Nirvana
分析流程中的Quality Control:
- single sample QC: (sample removal)
- fingerprint concordance between the array and WGS data (selected 113 sites)
- sex concordance (seq result vs. self-report)
- cross-individual contamination rate (related to call rate) by counting number of reads at common homozygous alternate SNP
- mean coverage (threshold of ≥30×)
- genome coverage (threshold of ≥90% at 20×)
- coverage of hereditary disease risk genes (threshold of ≥95% at 20×)
- aligned Q30 bases (threshold of ≥8 × 1010)
- joint callset QC: (similar to that of gnomAD 3.1, only flagged as failing QC)
- population outlier through PCA
- variant hard filters ex: GQ, DP, QUAL flags, PASS filter…
- VQSR
- relatedness: kniship calculated by Hail
Workflow Benchmarking
使用 GIABv4.2.1 truth set: HG001(NA12878), HG003, HG004(parents of AJ trio), and HG005(son of Han trio) 從下表的比對結果可知,All of US workflow 在 SNV/indel 的 Precision 超過 99%,代表偵測到的變異幾乎都為真( QC 做得很好,顯著降低false-positives)

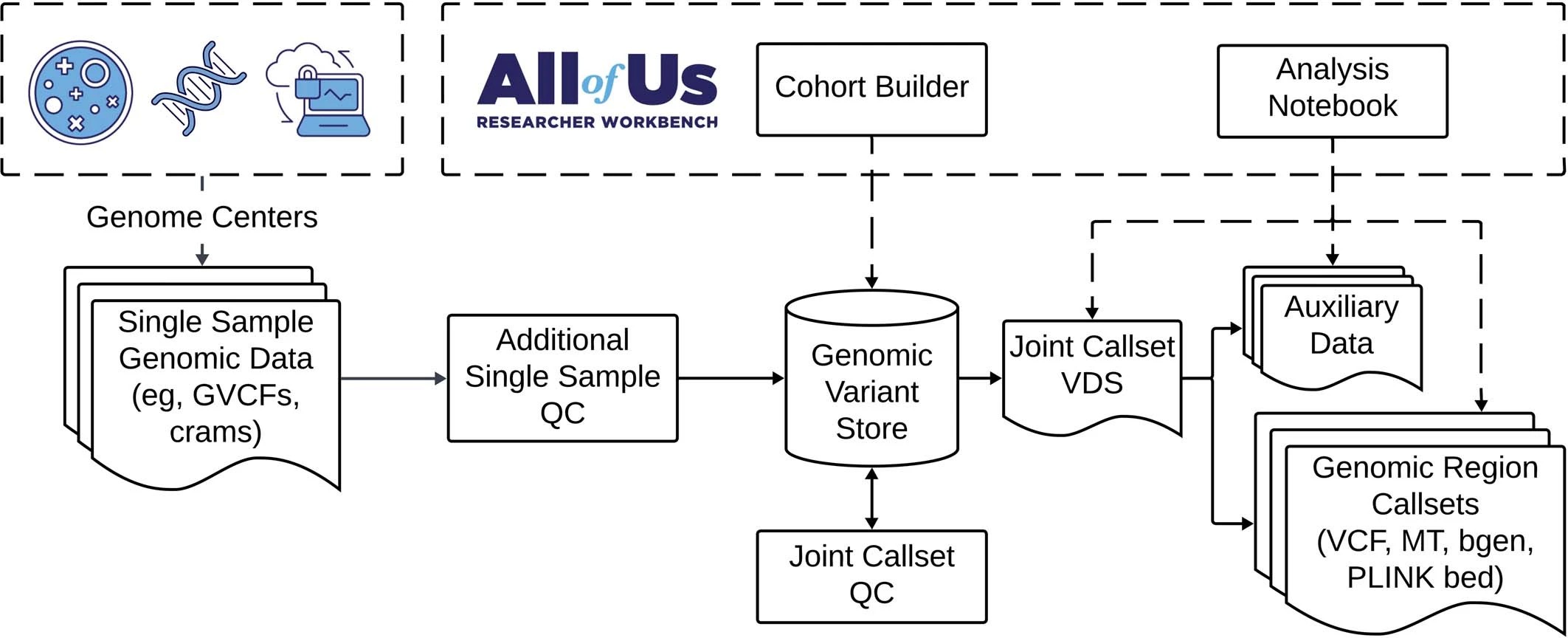
雲端式共享空間
All of US 官方網站 依照使用者身分與目的提供不同資源,主要分兩大類:

- Data Broswer: 開源的族群性(aggregate-level data)統計成果
以 GENOMICS VARIANT 為例,可用基因名稱、rs number 甚至是基因區段搜尋族群偵測到的變異位點,下圖示範以TP53搜尋結果

網站很讚的地方是提供客製化的篩選(圖中黃色標示處),可以用註釋結果如 VEP consequence, ClinVar, 或族群頻率如allele count threshold 等篩出感興趣的位點。此外點選ID還有更詳細的統計,跟gnomAD broswer有得拚! 但目前網站只提供瀏覽功能,還沒找到export 按鈕
- Researcher Workbench: 若學術單位或研究者想使用資料,只要申請平台使用權,購買credit(儲存空間分析費用),即可自由在雲端workspace下開創 project、上傳資料和使用pipeline。
雲端分析的另一優點即是節省各自備份或傳輸資料的開銷:
Storing one copy per institution of this data at 556 registered institutions would cost about US$1.16 billion per year. By contrast, storing a central cloud copy costs about US$1.14 million per year
近期研究成果
2024年2月團隊於 Nature 期刊發表最新研究成果:
The All of Us Research Program Genomics Investigators. Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program. Nature 627, 340–346 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06957-x
現階段收案情況與重點成果:
- release of 245,388 clinical-grade genome sequences, and identified more than 1 billion genetic variants
- new genotype-phenotype associations using longitudinal electronic health record
- Summary-level data are publicly available, and individual-level data can be accessed by researchers
Variant discovery in joint callset
- 將joint callset結果和dbSNP v153版資料庫位點比對,分別在 non-coding 跟 coding region 找到 272,051,104 和 3,913,722 個新位點
- 依照族群 MAF 分類發現 99.98% 的 coding variants 屬於 MAF < 1% 的罕見變異(rare variant);有趣的是找到 0.01% 變異的屬於在非歐洲族群普遍(MAF > 1%),但單看歐洲族群屬於罕見的變異位點
- 利用illumina Nirvana (DRAGEN implemented annotation tool) 進行註釋,並統計不同族群具有被 Clinvar 判定為 Likely Pathogenic 以上的位點數,利用OR、p-value等數值衡量後,發現歐洲族群發現rare pathogenic variant的比例最高,其他族群可能受限於樣本數大小而降低統計結果的顯著性。

Ancestry and relatedness
問卷的族群統計有 51.1% 屬於非歐洲族群,使用基因資訊進行族群分類:
分類方式參考gnomAD資料庫的做法:
training a random forest (RF) classifier on a subset of samples with provided genetic ancestry labels using the principal components from the PCA as features.
使用 HGDP and 1000 Genomes 計畫樣本作為 training set,並從 gnomAD 資料庫取得變異位點資訊當作PCA input,clustering 後取前 16PC 當作 random forest input,並輸出族群分類結果。
將模型套用至 All of US 3202 個樣本上,發現問卷回答之族群(self-reported ethnicity) 與基因預測之族群結果一致性達87%
Genotype-by-phenotype associations
大量的樣本與 variant genotype 很適合做GWAS,以 LDL-C phenotye 為例,從 manhattan plot 看到許多顯著關聯的位點,和過去從TOPMed資料庫偵測之顯著關聯位點做關聯性比較,發現兩計畫的beta (odds ratio) 值高度相關,代表位點對特徵的趨勢一致。但由於統計模型、族群組成的不同,使每個 variant loci 的 effect size 不同。
此外也參照 phenotype-genotype reference map (PGRM) 來驗證 All of US 做 PheWAS時,能否重現(replication)相同的顯著關聯結果
phenotype-genotype reference map (PGRM), a set of 5,879 genetic associations from 523 GWAS publications that can be used for high-throughput replication experiments.
PGRM 如何定義replicated?
Replication: an association with a p value < 0.05 and OR in the same direction as the original study.
PGRM 另一特別之處在於有族群特異的association,可以個別比對不同族群差異,最終在power > 80% 的 association type 下,不同族群有成功 replicate 的比例分別為: 72.0% (18/25) in AFR, 100% (13/13) in AMR, 46.6% (7/15) in EAS, 74.9% (1,064/1,421) in EUR, and 100% (1/1) in SAS.
這裡EAS重複狀況較差,可能和genetic loci boosting, EHR data updation等因素有關,而改變統計結果。
Comments
All of US 計畫的執行力高,並持續增進收案基數,對於族群基因體學的影響大,且過程中為因應資料量龐大的議題,會額外討論如資料保存、壓縮效率、以及位點QC等,對於之後有興趣做族群基因體分析者,可作為重要參考。這麼大的資料,若能持續的做追蹤並紀錄general population 是否有疾病發生,對長期研究也能有貢獻。當然維持計畫需龐大資金與研究者投入,相信NIH主持的計畫可以相當長壽。
就族群多樣性的議題來說,USA多族群歷史較長,或許也挺適合觀察mixed-population後變異的特徵是否有保留或改變,甚至新發變異等議題;而本篇文章並沒有特別討論long-read和short-read data訂出來的樣本結果差異,但相信定序技術發展,當long-read使用越頻繁,就能將探討主軸從SNV延續至SV, CNV等大片段類型上。
References
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06957-x https://www.ghd.tw/Home/International_data_standards https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/allofus/vignettes/data.html
